Smithers Pira forecasts industrial printing market to grow to $114.8 billion by 2022
Industrial printing takes place across the world, with manufacturers using the processes, and specialist suppliers selling to component and product manufacturers.
Industrial and functional printing applications are all seeing growth with sectors including décor and laminates; ceramics; electronics, including displays and photovoltaics, glass, aerospace and automotive, biomedical, promotional and miscellaneous items, 3D printing and inkjet printed textiles. All of these are printed by a variety of specialist analogue methods and inkjet.
In ‘The Future of Functional and Industrial Print to 2022’, Smithers Pira values the current market at $76.9 billion, up from $37.2 billion in 2012, but with further growth forecasted to $114.8 billion by 2022.
"Suppliers have developed new equipment that widens the applications, with new inks, coatings and functional fluids providing new properties of flexibility, adhesion and durability, together with novel capabilities in electronics and biomedical to provide specific actions," commented report author Sean Smyth.
"While analogue printing methods – gravure, flexo, litho, screen, pad printing and foiling – are widely used, there is very strong growth in digital methods, with new inkjet inks and fluids opening many new opportunities."
"These markets do not use paper or paperboard substrates, but rather plastic, film, glass, wood, metal, ceramics, textiles, laminates and composite materials are involved. In the case of 3D printing there are plastics and metals, with some composites," Smith added.
Industrial printing takes place across the world, with manufacturers using the processes, and specialist suppliers selling to component and product manufacturers. Routes to market vary widely, with large manufacturers employing printing functions as part of their processes, and specialist print businesses supplying components.
Asia is the largest region, reflecting the concentration of manufacturing there, with large printing companies supplying electronics and environment materials, films and interior décor materials; and it is home to many giant electronic companies using printing as part of the manufacture of membrane switches, tags, circuitry, displays and photovoltaics.
There is also strong growth in North America and Western Europe for high-value items and as improvements to many manufacturing processes. New technologies are being developed in these regions, with inkjet textile bringing high-value, short-run textile printing closer to the end user; while 3D printing is enabling changes to some manufacturing and potentially changing business models through distributed 3D printing on-demand.
Printing may be used as part of a wider manufacturing process or, in the case of 3D additive printing, it can be the manufacturing.
The required skillset for this print is probably less than in commercial print or packaging; prepress production is often outsourced with screens, plates and cylinders bought in as required and reused over many years.
The management of the industrial plant will concentrate on improving the methods of making the product rather than the intricacies of print technology. There is also much activity in developing routes to market, for print suppliers and equipment manufacturers, and for associated consumables supply.
Topics
Interested in joining our community?
Enquire today about joining your local FESPA Association or FESPA Direct
Recent news

The Rise of B2B in Print-On-Demand: Mastering Personalisation to Drive Growth
Rusty Pepper highlights the B2B shift in Print-On-Demand, focusing on personalisation's role in driving growth. He discusses market differences between Europe and the U.S., challenges in global scaling, and strategies for successful implementation. Experts will share insights at FESPA 2025, covering automation, fulfilment, and market trends.

Navigating the Evolving Landscape of Fashion, Print and Sustainability
In this podcast, Debbie McKeegan and April Holyome – head of Product at the luxury Italian brand 16Arlington discuss the evolving landscape of fashion at the Epson Textile Academy.
.jpg?width=550)
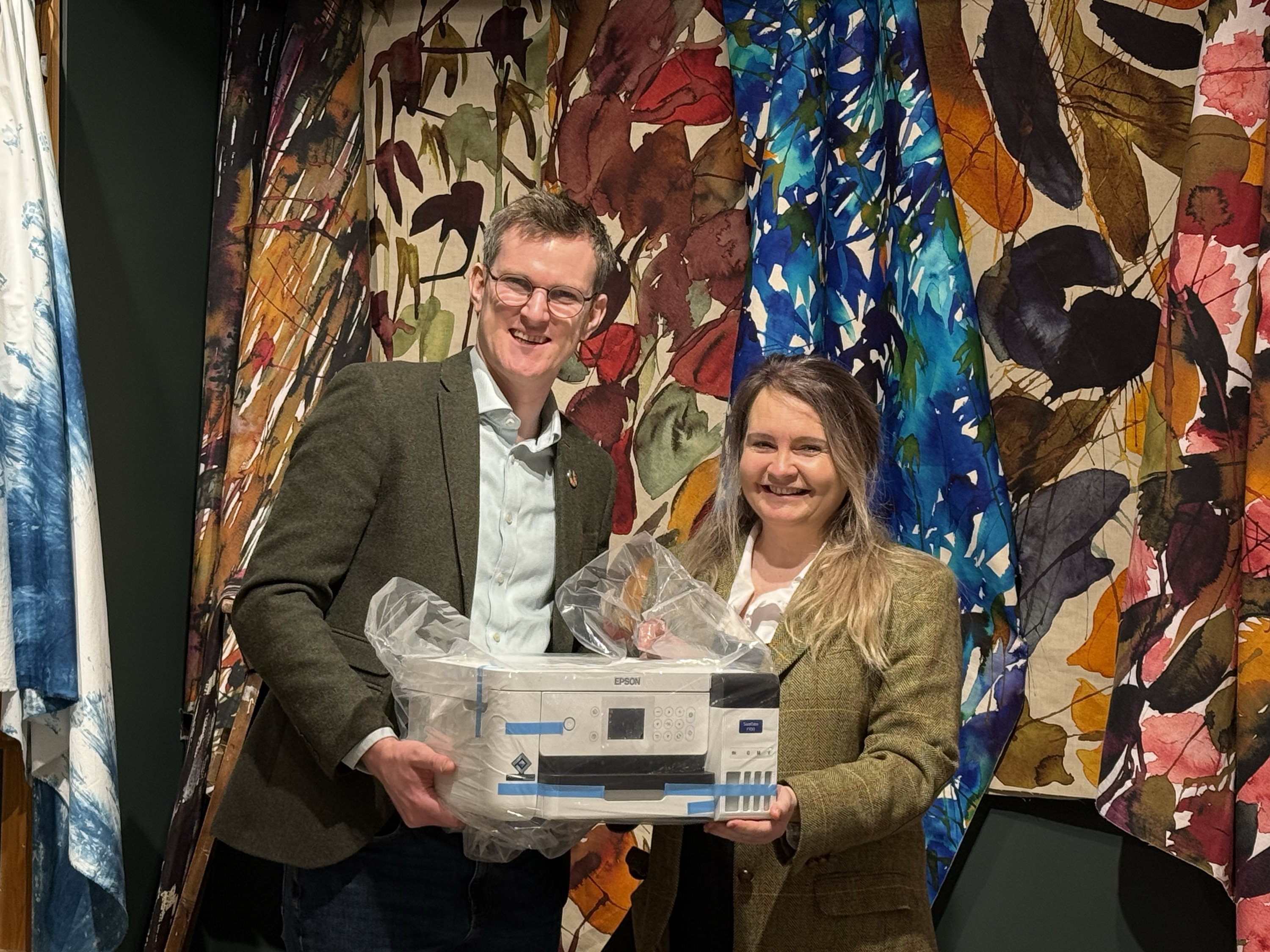
Awarding Talent: Joanne O’Rourke Wins the Epson Eco Stories Textile Challenge and Trip to FESPA 2025
Joanne O'Rourke won the Epson Eco Stories Textile Challenge, receiving an Epson SureColor SC-F100 printer and a trip to FESPA 2025 in May. The award highlights the importance of supporting emerging designers for a sustainable print industry. These "digital natives" drive innovation, sustainability, and technological advancement, crucial for the sector's future.

The importance of Personalisation in Direct Mail - The Power of Print
Jeroen van Druenen, CCO of Jubels discusses how personalised direct mail, especially print, boosts engagement and ROI by tailoring content to individual recipients. Using variable data printing (VDP), marketers create unique designs and offers, enhancing relevance and fostering stronger customer relationships. Physical mail's tangibility and lasting impact further amplify personalisation's effectiveness.