How PDFs implement ICC colour management
Paul Sherfield provides a user overview of how PDFs implement ICC colour management when creating and processing these files.
What is an output intent?
This article will give a user’s overview of how PDFs implement ICC colour management when creating and processing these files.
Before reading this article it would be best to look at the piece I wrote on PDF/X and its use in the wide format sector and markets.
Creating PDF files for print
Most PDFs supplied to printers will have been produced by creators using software such as Abode CC InDesign and Illustrator, Affinity Publisher, Quack Express and CorelDraw.
All of these page creation software’s will have the PDF pre-set, including the PDF X versions and use the Adobe PDF libraries or similar to produce files with needed to produce a Postscript file first.
Looking at the Adobe CC suite, colour management settings in all applications can be synchronised in the Bridge application
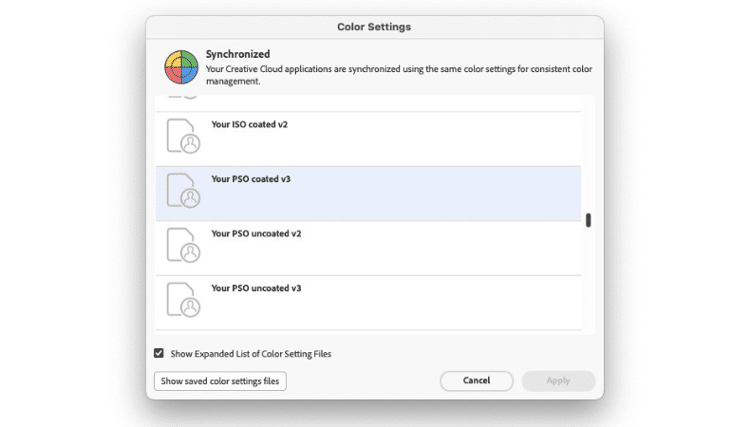
 Under the ‘Edit’ menu in Adobe Bridge you will find the ‘Color Settings’ panel. If you have not used this before it may display ‘Not Synchronised’ at the top of the panel. This means that your colour management settings are not the same across all the Adobe CC applications, including Acrobat and PDF’s produced, which can result in unexpected changes in colour.
Under the ‘Edit’ menu in Adobe Bridge you will find the ‘Color Settings’ panel. If you have not used this before it may display ‘Not Synchronised’ at the top of the panel. This means that your colour management settings are not the same across all the Adobe CC applications, including Acrobat and PDF’s produced, which can result in unexpected changes in colour.
From the list of color setting files (.csf) shown, select the one you wish to use, in this case a custom color settings file*, and click on ‘Apply’. This will then instruct Adobe CC to use this color setting file across the entire Abode CC suite.
 With this in place, now when saving to a PDF X from Adobe InDesign, this color setting will be used.
With this in place, now when saving to a PDF X from Adobe InDesign, this color setting will be used.
*Note this color setting file is a custom one and not in the standard Adobe CC color settings. These custom color settings can be easily produced in Adobe Photoshop.
 Above is the ‘Export Adobe PDF’ panel from Adobe InDesign, the PDF X4 export settings have been selected and as can been seen, a little modified.
Above is the ‘Export Adobe PDF’ panel from Adobe InDesign, the PDF X4 export settings have been selected and as can been seen, a little modified.
This is because the standard in the ‘Color Conversion’ box is set to ‘No Conversion’. In this the Convert to Destination’ is recommended, selected from the drop down. This will convert to CMYK profile that has been synchronised using the Bridge color setting tool as described above.
This will convert all images to this profile including RGB images, so saving converting in an image editor such as Adobe Photoshop. It with also embed this profile as a PDF X output intent which is used to describe the printing condition for which the PDF is intended. It then does not need to embed the ICC profile in every image in the file, so reducing the file size.
Processing PDF files at the print supplier
The PDF X4 produced using the synchronised colour management settings and having the PSO coated v3 profile as the output intent should process correctly on the many digital end ends (DFE’s) used by wide format printers.
However, the way that colour management is implemented in these DFE’s can vary. The setting used in the above illustration are for coated papers and based on an offset litho standard, sometimes referred to as FOGRA 51. If this is what you wish to simulate, and it matches the printers colour management policies and workflows then no problems. Indeed, most DFE’s have a function that can be implemented to honour the PDF X output intent.
The colour issues arise when the colour managed PDF X4 does not match the printers colour workflows and the substrates used.
While PSO coated v3 (FOGRA 51) is a good starting point, the many differing substrates used and required by the myriad products and markets served by the wide format sector require co-operation between the content creator and printer in order to ensure the colour result is as expected.
This may mean using other ICC profiles as the output intent, such a those for uncoated papers. It is possible that the printer, using systems such as colour servers or advanced colour management tools in their DFE, may be able to convert the supplied PDF X4 file to the correct profile for the substrate.
Again, the creator should talk to the printer.
Device profiles
None of the above will result in the very best colour reproduction without the use of device profiles by the printer.
This is an ICC profile that describes the way the specific digital press will reproduce colour using the specified ink and the chosen substrate.
A range of pre-made profile are often supplied and installed in a digital printing devices on installation, however these can only cover some types of substrates and/or not optimal if the very best colour reproduction is needed.
The printer should have the colour management software and hardware, together with the knowledge needed to make the custom device profile needed for their clients, substrates, printing devices and markets.
These device profiles then work within the DFE’s colour management tools with the agreed profile/output intent to simulate the agreed ICC profiles/output intents in the PDF X4.
If there is no need to simulation a CMYK ICC profile such as PSO coated v3, the printer may request your PDF’s in a RGB colour space, then then use the device profile to process to the maximum colour gamut of the press. There will be a further article on this area and wide gamut printing.
Conclusions
The creator should talk to the supplier at each stage of the process in order to, as FOGRA say, ‘Print the Expected’.
- Ensure that a correct PDF X4 with the agreed output intent is supplied.
- Agree with the printer if any further colour management changes will be processed by them to suit the substrates used.
- Ensure the printer can produce and use the correct device profiles for your production and substrates used.
Topics
Interested in joining our community?
Enquire today about joining your local FESPA Association or FESPA Direct
Recent news

The importance of Personalisation in Direct Mail - The Power of Print
Jeroen van Druenen, CCO of Jubels discusses how personalised direct mail, especially print, boosts engagement and ROI by tailoring content to individual recipients. Using variable data printing (VDP), marketers create unique designs and offers, enhancing relevance and fostering stronger customer relationships. Physical mail's tangibility and lasting impact further amplify personalisation's effectiveness.

What are the current trends for digital screens?
Digital screens are evolving rapidly, moving beyond simple signage. MicroLED technology improves resolution and efficiency, while 3D and AR displays offer immersive experiences. AI is transforming content creation and analytics, personalising interactions and optimising screen placement. Larger, wall-sized screens and temporary rentals at events are becoming more common. As screens become ubiquitous, innovation focuses on eye-catching solutions to maintain audience engagement.

Hints and tips for vehicle wrapping success
While rising demand for vehicle wrapping is good news for the industry, this is placing more pressure on companies to deliver quality work at a solid pace. Here, Rob Fletcher picks up some tips from several experts in this sector to help wrappers operate smoothly.

What are the opportunities in Personalisation for Sportwear and Signage?
Rob Fletcher discusses the growing importance of personalisation and digital innovation across sectors. Major brands use personalised print to engage customers and boost sales. Personalised sportswear demand is increasing, and companies like Eurojersey embrace sustainable manufacturing and digital transformation.