The use of mercury lamps on the decrease
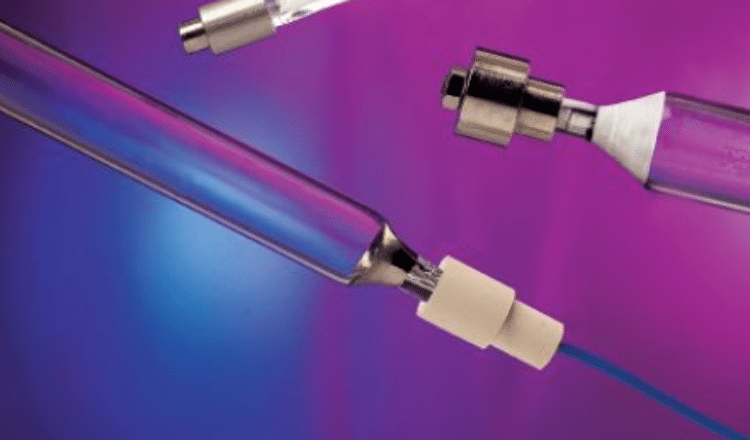
Laurel Brunner shares the ongoing trend of mercury lamps being less and less used across the printing industry. Governments and bodies around the world are now banning the use of mercury in products by the end of 2025.
It’s been a long time coming but the end of mercury arc lamps is definitely in sight. Mercury is a seriously nasty neurotoxin that is steadily being regulated out of products, including in the fluorescent lamps used in the printing industry for ink curing. Bodies from the US Environmental Protection Agency to the United Nations and the European Union are all banning the use of mercury in products mostly by the end of 2025.
UV curable ink chemistries have been optimised for curing using mercury arc lamps for decades, so the mercury arc lamp habit is well-entrenched in the printing business. The lamps have been the workhorses of curing applications and used in a wide range of applications for many years. But times and technologies change. The good news is that we have a solid market in LED curing lamps and inks. Printers still using technologies that use mercury should be thinking about making the leap into LED. Fluorescent lamps will be around for the next couple of years, but the printing needs to accelerate its adoption of LED based alternaties for ink curing. The end of 2025 marks the end of exemptions for the use of mercury in products such as fluorescent lamps.
Printers have a few options, such as stockpiling replacement lamps which quite a few companies are doing. But this ties up capital, distorts the market, and only defers the inevitable. Far more sensible is to make the transition now and to get used to the new reality. Fortunately LED lamps have several compelling attractions, in that they require barely any time to warm up and last far longer than fluorescent lamps. They can deliver an extremely smooth spectral curve that can be read without needing a high resolution measurement device. They also generate much less heat, so the range of substrates that can be printed is greater. And with LED lamps there is no risk of UV radiation which isn’t good for your health.
New investment carries its own risk, but when it comes to inks and curing, staying within the rules has to be a good idea. The matter of mercury arc versus LED can get complicated, so it’s also good that regulations have simplified the argument. Banning the use of mercury is in the interests of us all, so we should welcome both the rules and the development of LED based alternatives. We should probably not dwell on the fact that there is probably more mercury in your mouth (800mg per dental filling) than in the average curing lamp (10-100mg). But that’s an altogether different concern.
Source Information: This article was produced by the Verdigris Project, an industry initiative intended to raise awareness of print’s positive environmental impact. This weekly commentary helps printing companies keep up to date with environmental standards, and how environmentally friendly business management can help improve their bottom lines. Verdigris is supported by the following companies: Agfa Graphics, EFI, Fespa, Fujifilm, HP, Kodak, Miraclon, RicohSplash PR, Unity Publishing and Xeikon.
Topics
Recent news
What are the benefits of print businesses committing to a Net Zero Carbon emissions target?
We speak to Robert Connell, Senior Commercial Sustainability Manager at ClimatePartner who who offer solutions along the net zero cycle to support business’s effort in corporate climate action. In this discussion we discuss the importance and the process and benefits of businesses committing to a Net Zero Carbon emissions target.

6 Sustainable Printing Practices Changing the Game in Textile and Apparel Decoration
The textile industry is shifting towards sustainability. Innovations like waterless and digital printing, eco-friendly inks, and recycled materials are reducing waste. AI and automation optimise production, while circular models promote reuse. Consumer demand for transparency drives this change, making sustainable practices essential for future-focused brands.

Sustainability in Production Print: Advancing Practices in Wide Format, Textiles, and Software
As sustainability continues to take centerstage across industries, the production print sector is making massive strides in integrating eco-conscious practices. From wide format to textile applications, with the growing reliance on advanced production software, the space is evolving to meet environmental goals as well as consumer demand for sustainable products.

Why must the print industry recognise software and material innovation
Laurel Brunner argues that the printing industry must recognise the value of both software and material innovation, and be willing to pay for it. Software, though intangible, drives efficiency and reduces carbon footprints. While materials science currently dominates, R&D costs are inherent in all advancements. Paying a premium ensures continued progress, benefiting the industry's evolution and sustainability.